MENU
Starting a Business
- Best Small Business Loans
- Best Business Internet Service
- Best Online Payroll Service
- Best Business Phone Systems
Our Top Picks
- OnPay Payroll Review
- ADP Payroll Review
- Ooma Office Review
- RingCentral Review
Our In-Depth Reviews
Finance
- Best Accounting Software
- Best Merchant Services Providers
- Best Credit Card Processors
- Best Mobile Credit Card Processors
Our Top Picks
- Clover Review
- Merchant One Review
- QuickBooks Online Review
- Xero Accounting Review
Our In-Depth Reviews
- Accounting
- Finances
- Financial Solutions
- Funding
Explore More
Human Resources
- Best Human Resources Outsourcing Services
- Best Time and Attendance Software
- Best PEO Services
- Best Business Employee Retirement Plans
Our Top Picks
- Bambee Review
- Rippling HR Software Review
- TriNet Review
- Gusto Payroll Review
Our In-Depth Reviews
- Employees
- HR Solutions
- Hiring
- Managing
Explore More
Marketing and Sales
- Best Text Message Marketing Services
- Best CRM Software
- Best Email Marketing Services
- Best Website Builders
Our Top Picks
- Textedly Review
- Salesforce Review
- EZ Texting Review
- Textline Review
Our In-Depth Reviews
Technology
- Best GPS Fleet Management Software
- Best POS Systems
- Best Employee Monitoring Software
- Best Document Management Software
Our Top Picks
- Verizon Connect Fleet GPS Review
- Zoom Review
- Samsara Review
- Zoho CRM Review
Our In-Depth Reviews
Business Basics
- 4 Simple Steps to Valuing Your Small Business
- How to Write a Business Growth Plan
- 12 Business Skills You Need to Master
- How to Start a One-Person Business
Our Top Picks
The Cost of Cybersecurity and How to Budget for It
Table of Contents
Cyberattacks on big corporations are certainly newsworthy. However, hackers frequently target small businesses in data breaches and other cyberattacks. Cybersecurity incidents can paralyze your business and destroy customer trust, and recovering from these attacks is expensive. To help prevent these devastating consequences, it’s crucial for businesses of all sizes to put cybersecurity safeguards in place.
Like many core business functions, cybersecurity incurs expenses. But how much should you budget for your company’s cyber defenses? We’ll look at best practices for cybersecurity budget planning, outline cyberattack costs, and share various types of cyber incidents to be aware of.
Why budget for cybersecurity?

Cybersecurity affects businesses of all sizes. According to Netwrix Research Lab’s 2023 Hybrid Security Trends Report, 68 percent of all organizations surveyed — large and small — had experienced a cyberattack in the past 12 months. More specifically, 43 percent of data breaches involved small businesses.

Here are some benefits of establishing a cybersecurity budget for your small business:
- Protecting your business: A cybersecurity budget funds programs that protect your company from a cyberattack’s costs and disruptions.
- Satisfying risk-assessment clauses: A funded cybersecurity plan acts as a safety measure for dealing with third-party cybersecurity risk assessments (or other vendor requirements). Risk-assessment clauses are becoming standard in contracts.
- Helping with compliance: Your cybersecurity budget will help you comply with regulations such as GDPR, PCI DSS, HIPAA and other national or state regulations that legally require companies to maintain cybersecurity standards.
- Keeping your company competitive: Your cybersecurity budget will help you compete for large projects or contracts.
What cybersecurity areas should your budget include?
The cybersecurity arena is massive. As you build your budget, consider the following investment areas that small businesses should prioritize:
- Risk assessment
- Business preparation and continuity
- Incident response
- Employee training
- Network and website vulnerability identification and management
- Regular scanning and testing, including dark web scanning and ethical hacking
- Cyber insurance policies
If you’re not convinced that your company needs a cybersecurity budget, consider that your business won’t be the only victim of a cyberattack; your employees, customers and strategic partners will experience the fallout as well. The only way to prevent an attack is to strengthen your understanding, posture and defenses — a process that merits investment for every small business.
Cybersecurity risk management is the process of identifying the specific risks your company faces and planning how you’ll defend against them. When you understand the risks, you can craft unique cybersecurity strategies to fit your situation.
How much should you spend on cybersecurity?
Cybersecurity spending is often tied to a business’s overall IT budget, which takes into account the company’s size and IT infrastructure. According to the 2023 State of IT report, 54 percent of companies globally plan to increase their IT budgets because of the following factors:

- Experiencing recent security incidents
- Updating older systems to shore up cybersecurity vulnerabilities
- Enhancing security software
- Spending more on managed security services
According to Statista, businesses worldwide spend an average of 12 percent of their IT budgets on cybersecurity. For example, if a company pays $3,000 monthly to an IT managed service provider to cover their IT needs, its cybersecurity budget would be about $360 per month.
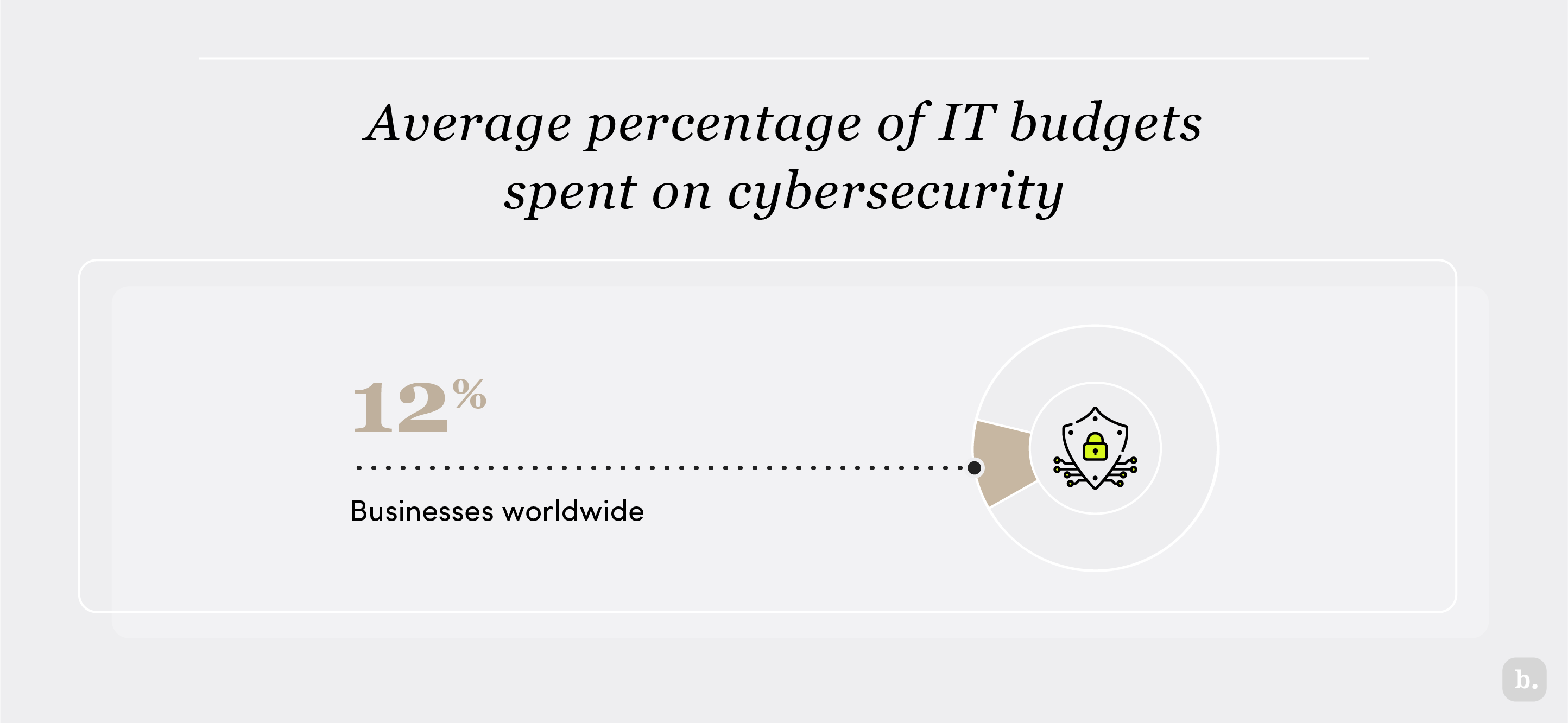
However, the percentage of total IT spending on cybersecurity will vary widely due to the following factors:
- Industry and company size
- Compliance and other mandates that affect your business
- The sensitivity of the data you collect, use and share
- Requests from company stakeholders or customers
Here are a few tips for deciding on your cybersecurity spending:
- Don’t spend a lot all at once. When you create a cybersecurity budget, you don’t have to invest a lot of money upfront. If you haven’t had a cybersecurity budget, try working a small amount into your upcoming budget. A little bit can go a long way; for a relatively small investment, you can take the critical first step of performing a cybersecurity risk assessment and start working on key improvements.
- Get advice from your cybersecurity provider. Your cybersecurity provider can help you identify your business’s highest-priority and lowest-cost action items. From there, you can tailor your cybersecurity program and slowly grow your budget to provide enhanced protection and mitigate risks. Your cybersecurity is an ongoing initiative, not a one-time project.
- Get company leadership on board. Small businesses often operate on tight budgets. In some cases, the person building and approving the budget may not understand the critical nature of cybersecurity. If you’re facing hesitation from leadership, stakeholders or the board of directors, perform a basic risk assessment to show them where your company stands and how an investment could bolster protection. Leadership — whether the board, C-suite executives or company owners — is responsible for guiding the company in the right direction, and that includes protecting it from threats.
Investing in employee training is crucial for any cybersecurity program. According to the World Economic Forum, human error causes 95 percent of cybersecurity breaches.
How much does a data breach cost?
Cyberattacks cause significant damage and expense. According to IBM’s 2023 Cost of a Data Breach Report, the average impact of a data breach on organizations with fewer than 500 employees is $3.31 million; the average cost per breached record is $164.
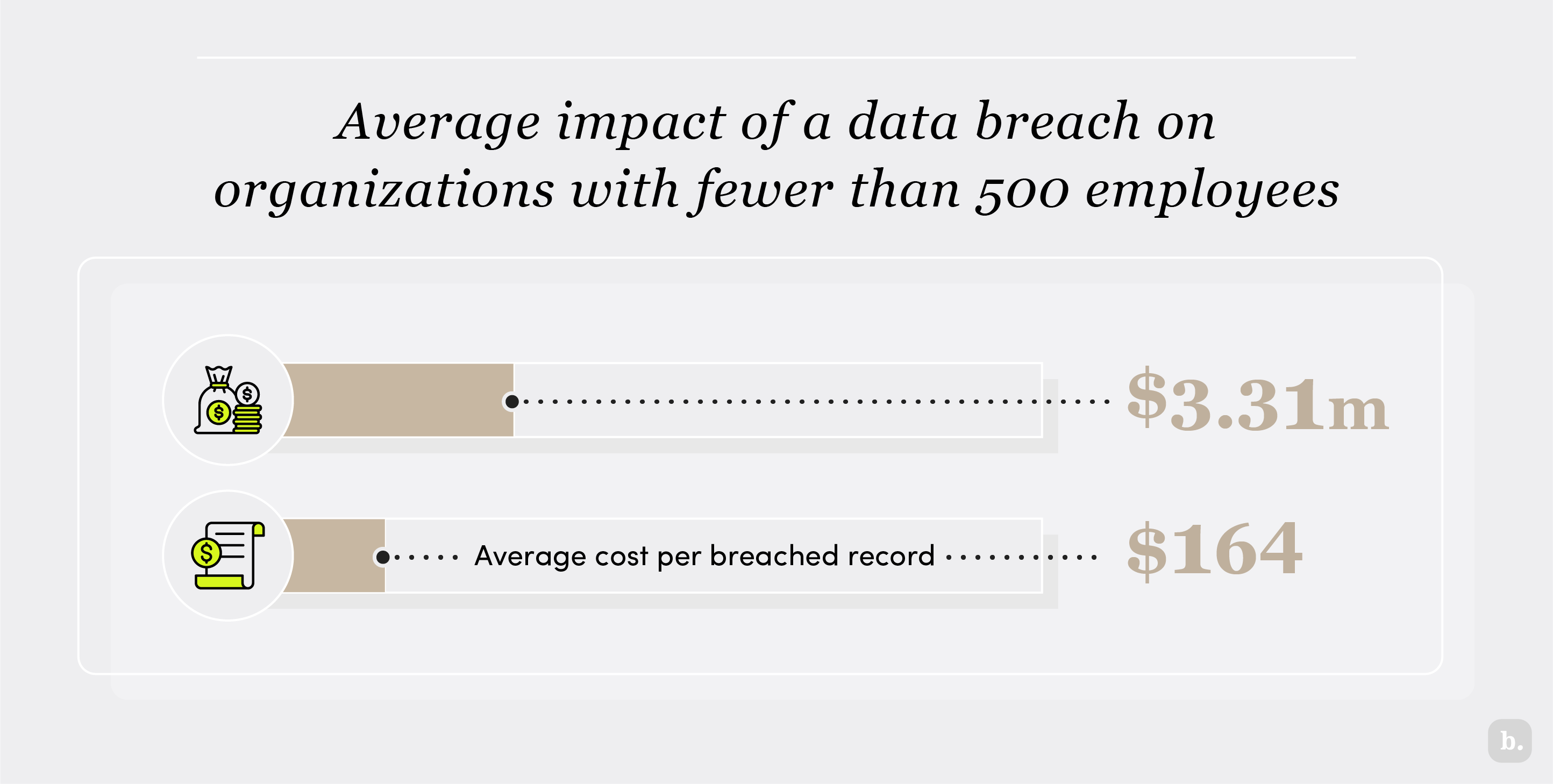
But the full cost of a data breach isn’t always immediately known. Potential direct costs include the following:
- Monetary theft
- Remediation and system repair
- Regulatory and compliance fines
- Legal and public relations fees
- Notification, identity theft repair and credit monitoring for affected parties
- Increase in insurance premium
Potential indirect costs include the following:
- Business disruption and downtime
- Loss of business or customers
- Loss of intellectual property
- Damage to company credibility, brand and reputation
Taking crucial cybersecurity steps can mitigate the damage and reduce the costs resulting from a data breach. These steps include having an incident response team and cybersecurity plan in place, using encryption, conducting employee training, and securing cyber insurance.
The concept of “cyber resilience” is growing in importance. Given the potential expenses and negative impacts of a data breach on a small business, any budget you dedicate to improving your company’s cybersecurity posture is well spent.
5 types of cyberattacks that threaten businesses
Your in-house IT team or outsourced IT partner should stay vigilant about the following cyberattack types. Some are obvious, while others are more overlooked attack vectors.
1. Denial-of-service (DoS) and distributed-denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks
A DoS attack is designed to overwhelm a machine or network’s resources so the intended users cannot access the system. DoS attacks are accomplished by bombarding the specified target with a flood of traffic or information to crash the system.
Unlike other types of cyber risks, DoS attacks do not directly benefit the attacker. A competitor may initiate a DoS attack to disrupt your website and gain an advantage, or it may be the first stage of a greater cyberthreat.
A DDoS attack is the same as a DoS attack but is launched from many host computers. A DDoS attack aims to overwhelm a company website or service beyond what the server can accommodate so that it malfunctions.
There are different types of DoS and DDoS attacks, but these are the most common:
- TCP SYN flooding: These attacks can be prevented by placing servers behind a firewall.
- Ping-of-death attacks: A ping-of-death attack can be prevented by placing a server behind a firewall.
- Teardrop attacks: Teardrop attacks result from a vulnerability that’s common in older versions of Windows; multiple patches have been issued over the years. Keep your operating system up to date to prevent teardrop attacks.
- Botnets: Botnets can be prevented by enabling RFC 3704 filtering and black-hole filtering.
2. Phishing and spear-phishing attacks
Phishing attacks are a common cyberthreat in which attackers send emails that appear to be from trusted sources. The goal is to gain personal information, like usernames and passwords, or to cause someone to take a specific action, such as downloading malware onto their machine.
A spear-phishing attack is similar, but instead of casting a wide net, attackers target individuals and take time to research victims and create personal, relevant messages.
The best way to prevent phishing attacks within your company is to train your staff on what to look for and how to spot risky emails and links.
Businesses are using machine learning to detect spear-phishing attacks by analyzing company social graphs, profiling user communication styles and analyzing email structure.
3. Man-in-the-middle (MitM) attacks
As the name implies, a MitM attack is when attackers insert themselves between a user and the services they interact with. MitM attack types include session hijacking, IP spoofing and replay attacks.
No single method can prevent all types of MitM attacks. However, encryption and digital certificates help prevent attackers from inserting themselves between users and servers.
4. Drive-by-download attacks
These attacks spread malware far and wide. An attacker looks for insecure websites to hack and plants malicious code throughout the site. When a user visits a hacked website, they may unintentionally install malicious code or be redirected to a site created by the attacker. Unlike other types of cyberthreats, a drive-by download doesn’t require the user to take an action, like clicking a button or opening an email, to be infected.
The best way to prevent this type of attack is to train your staff to keep their internet browsers and operating systems updated and to avoid insecure websites.
5. Password attacks
Obtaining a user’s password is among the oldest, most common and most effective cyberattack forms. Hackers can steal passwords in several ways:
- Watching someone type in their password
- Searching for unencrypted passwords on a network
- Using social engineering to reconstruct passwords
- Guessing a correct password through brute-force or dictionary attacks.
To protect your company from password attacks, implement two-factor authentication policies; require your employees to use strong, unique passwords; and implement a policy that locks user accounts after several invalid password attempts.
Cybersecurity can mitigate — but not eliminate — attacks
Cybersecurity is no longer a “nice to have” — it’s a must-have for businesses and a necessary budget item. A comprehensive cybersecurity program doesn’t have to cost a lot, but it requires prioritization and commitment from leadership, IT and other employees.
No matter how much you dedicate to cybersecurity, however, there are no 100-percent protection guarantees. Your best bet is to deploy a multifaceted, ongoing cybersecurity program using a combination of resources, testing, training and time.
The cost of a comprehensive cybersecurity program is a small price to pay for the peace of mind you’ll enjoy knowing that your company is better protected.
Jennifer Dublino contributed to this article.







