MENU
Starting a Business
- Best Small Business Loans
- Best Business Internet Service
- Best Online Payroll Service
- Best Business Phone Systems
Our Top Picks
- OnPay Payroll Review
- ADP Payroll Review
- Ooma Office Review
- RingCentral Review
Our In-Depth Reviews
Finance
- Best Accounting Software
- Best Merchant Services Providers
- Best Credit Card Processors
- Best Mobile Credit Card Processors
Our Top Picks
- Clover Review
- Merchant One Review
- QuickBooks Online Review
- Xero Accounting Review
Our In-Depth Reviews
- Accounting
- Finances
- Financial Solutions
- Funding
Explore More
Human Resources
- Best Human Resources Outsourcing Services
- Best Time and Attendance Software
- Best PEO Services
- Best Business Employee Retirement Plans
Our Top Picks
- Bambee Review
- Rippling HR Software Review
- TriNet Review
- Gusto Payroll Review
Our In-Depth Reviews
- Employees
- HR Solutions
- Hiring
- Managing
Explore More
Marketing and Sales
- Best Text Message Marketing Services
- Best CRM Software
- Best Email Marketing Services
- Best Website Builders
Our Top Picks
- Textedly Review
- Salesforce Review
- EZ Texting Review
- Textline Review
Our In-Depth Reviews
Technology
- Best GPS Fleet Management Software
- Best POS Systems
- Best Employee Monitoring Software
- Best Document Management Software
Our Top Picks
- Verizon Connect Fleet GPS Review
- Zoom Review
- Samsara Review
- Zoho CRM Review
Our In-Depth Reviews
Business Basics
- 4 Simple Steps to Valuing Your Small Business
- How to Write a Business Growth Plan
- 12 Business Skills You Need to Master
- How to Start a One-Person Business
Our Top Picks
Table of Contents
There’s an old saying in software development that goes something like, “Fast, good or cheap — pick two.” Known as the iron triangle, project management triangle, or triple constraint, this concept is familiar to anyone who has ever felt the pressure of weighing the opposing forces of quality, speed and cost against one another.
The general concept is that you have three choices when making a product: make it quickly, cheaply or well. While it has long been believed that it isn’t possible to accomplish all three, some now think it is. Focusing on values and eliminating assumptions are key to developing a valuable product.
What is the iron triangle?
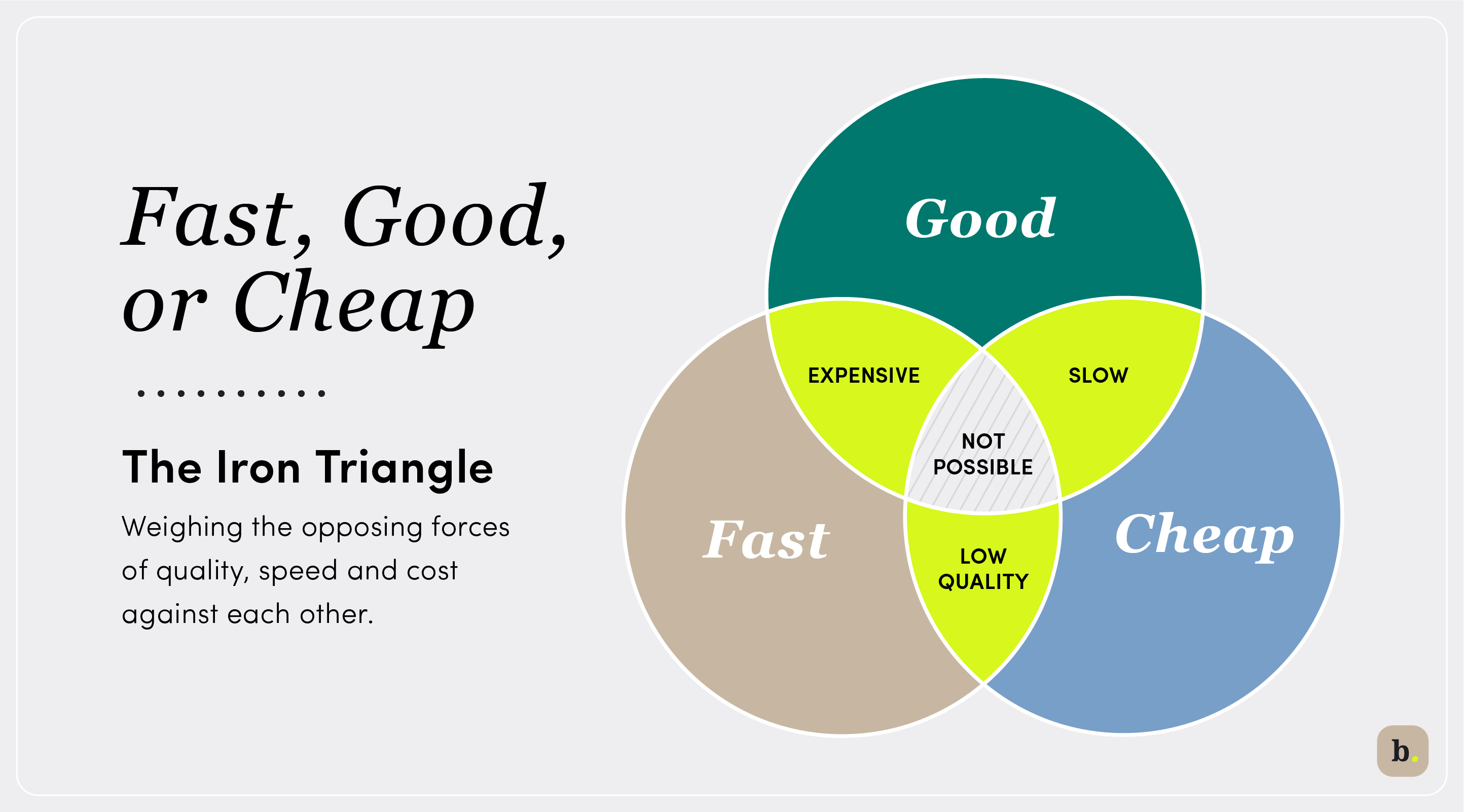
The concept of the iron triangle has evolved from these general assumptions:
- You can develop something quickly and of high quality, but it will be very costly.
- You can develop something quickly and cheaply, but it will be of low quality.
- You can develop something of high quality and low cost, but it will take a long time.
Let’s look at each of these statements and what they mean for product development.
Cheap and fast
If you develop something cheap and fast, you’ll sacrifice features or the quality of the product to get it done quickly. You create an acceptable prototype and can start receiving feedback on it immediately.
This allows you to receive feedback and improve your product, but the sacrifice may not be worth it. You could hurt your company’s credibility and create more problems for yourself down the road.
Good and cheap
Another option is to create a high-quality product but spend as little money on it as possible. You’ll deliver a better product to your customers, but it could take a long time to finish it while staying under budget.
If you have the time to do a lot of research and product development in the beginning, this could have better results for your company. But in today’s market, businesses need to be flexible and able to act quickly, which isn’t likely with this method.
Ultimately, because you never received feedback from your customers during development, you may create a high-quality product they don’t want.
Good and fast
Finally, you can create a high-quality product in as little time as possible. Out of the three options, most businesses prefer this one. You can create a good product in a short time, but it’s going to cost you.
You’ll likely have to invest in a team to help you meet the demands of your timeline, and the extra money you spend could be wasted if you have to redo the product.
If you’re looking to master these three features, here are some product creation tips from seasoned entrepreneurs.
What are the problems with the iron triangle?
As you can see, a few problems emerge pretty quickly with these statements. The first issue with the iron triangle is the definition of “good,” or the concept of quality.
The triangle assumes that “fast and cheap” is an option, but in truth, delivering a low-quality product is seldom an actual option. Whether you’re releasing a product to market, completing a project for a client or delivering on an internal company project, quality is a universal expectation.
The second issue is known as the “mythical man-month” or Brooks’ law, which states, “Adding manpower to a late software project makes it later.” While Brooks’ law refers specifically to software development, the concept applies to many types of projects.
This is often simplified by the metaphor “too many cooks in the kitchen.” The basic concept is that when you add more people to a problem, the additional communication overhead and complexity of team dynamics often have a negative effect on the timeline as a whole.
That pretty much eliminates the combination of good and fast as a real option. That leaves us with good and cheap, but that means the project will take a long time. However, that doesn’t have to be the case if you use the lean method.
Although product cost and manufacturing time are essential, some level of product quality will always be expected if you want people to be satisfied with your products. Here are five reasons why product quality is important.
What is the lean startup method?
As mentioned above, the problems with the iron triangle leave us with one real option for product development: good and cheap. While this typically results in a slower development process, the lean startup method can help to speed things up.
The lean startup method, developed by Eric Ries in 2008, is a process for delivering products and businesses. Chronicled in Ries’ 2011 book The Lean Startup: How Today’s Entrepreneurs Use Continuous Innovation to Create Radically Successful Businesses, it is based on concepts borrowed from lean manufacturing as developed by Japanese automakers in the 1980s.
The lean startup method extols the concept that anything that does not deliver value to the end user is waste. This waste is combated by creating testable and measurable hypotheses, and then measuring them against honest and meaningful key performance indicators (KPIs). [Read related article: 14 Tools to Track Key Performance Indicators for Your Business]
The first step is to build a minimum viable product (MVP), which is the simplest version of a product that can test your hypothesis and deliver the maximum amount of validated learning.
After creating your initial MVP, the next step is to iterate repeatedly, using tools like split testing and the predetermined KPIs. These tools will help you adjust that product with one of two outcomes: refine it to excellence, or determine failure and pivot.
Under the lean method, anything that isn’t of value to the customer is considered waste. You utilize this method by creating hypotheses that you can test with a simple prototype of your product, allowing you to make improvements with minimal waste.
What is an example of the iron triangle?
The constraints (fast, good and cheap) are thought to be “iron” because you cannot change one constraint without affecting the others.
Let’s use the iron triangle to look at the constraints in project management for a software development team as an example. These are some of the constraints they’d face:
- The scope of the work (i.e., the functions and features necessary to deliver a working product)
- The necessary resources (i.e., the team members and budget for delivering and executing the product)
- The time it takes for the team to go to market and release the product
The goal of the iron triangle is to give a product team the necessary information to make trade-offs that ultimately help the business. For instance, if the team has a fixed scope, they may be halfway through the project and realize they are unable to meet the release date.
At that point, these are their options:
- Accept a later release date (time)
- Add more people to the project, ultimately raising the overall costs (resources)
Between 75 percent and 95 percent of product launches fail each year, according to LinkedIn. One of the most common mistakes that lead to product failure is not validating your product idea before launching it.
How can you apply the lean process?
Armed with what we’ve learned about the shortcomings of the iron triangle, it is possible to deliver a fast, cheap and good project by applying the concepts of the lean process. With this process, you keep teams small, because you know that too many cooks are going to make communication more difficult and limit your flexibility to deal with changing market demands.
Because you are just building an MVP at first, a significant upfront investment isn’t necessary. You are testing your hypothesis, so spending a lot of money or investing in other resources would be a waste if you’re wrong.
Keeping teams small and limiting the investment in the MVP lets you keep the project cheap. You’re also building the MVP to gain validated learning as soon as possible and deliver value to the end user.
By focusing on those values — and preventing a bloated scope full of assumptions and untested hypotheses — you can build fast. When limiting the work to the MVP, you get to market quickly with something of value.
Once you’ve released the initial MVP, you can continue to follow the lean principles, using validated learning and KPIs to decide what’s working and what’s not, and iterate quickly. The reiterations and meaningful measurements will guide you toward the end goal of delivering a good product.
And there you have it: fast, good and cheap, all in one project.











